‘We Demonstrated That HSE University Can Not Only Build a Satellite, but Maintain Its Operation’

The first HSE University satellite has completed its work in orbit after more than 35,000 hours of trouble-free operation, one billion kilometres travelled (24,600 orbits around the Earth), and hundreds of full-frame shots taken of the Earth's surface across an area of 320,000 km2. The HSE News Service shares the results of the satellite’s mission and the team’s plans for the near future.
The CubeSX-HSE and CubeSX-Sirius-HSE satellites were the first CubeSats launched by HSE University and the Sirius Educational Centre. The global SatNOGS catalogue now lists both devices as ‘Decayed,’ officially signalling the completion of a four-year orbital mission—three times longer than their formal one-year warranty and almost double the statistically reliable limit for standard CubeSat platforms.
Launched on March 22, 2021, on a Soyuz-2.1 commercial flight with a Fregat unit, the pair of three-unit satellites entered a Sun-synchronous orbit about 550 km high alongside three dozen more satellites. The initial estimated life of the OrbiCraft-Pro platform—12 months of active operation—was chosen as a compromise between expense and statistics; according to industry estimates, the probability of maintaining the functionality of a classic CubeSat a year after launch does not exceed 60%. This makes the final outcome all the more impressive: a four-year, trouble-free marathon spanning about one billion km (24,600 orbits), the equivalent of several dozen round trips from Earth to Mars. The final descent began in April–May 2025, when the perigee of both vehicles dropped below 200 km; the calculated models showed a linear increase in aerodynamic drag.
The main scientific programme was carried out by the world's first flat harmonic diffractive lens, with a diameter of 10 mm and embedded in a 3D-printed metal camera box. A series of calibration surveys proved that ultrathin optics produce an image comparable to classical refractive optics; the results are described in an article in Remote Sensing 14 (9): 2230 (2022). In total, the pair of satellites collected more than 320 full-frame shots of the Earth's surface, from the cellular clouds of the Barents Sea to the spring flood on the Volga, with a total area of over 300,000 km2, a milestone recorded by the HSE team at the three-year mark of the mission.
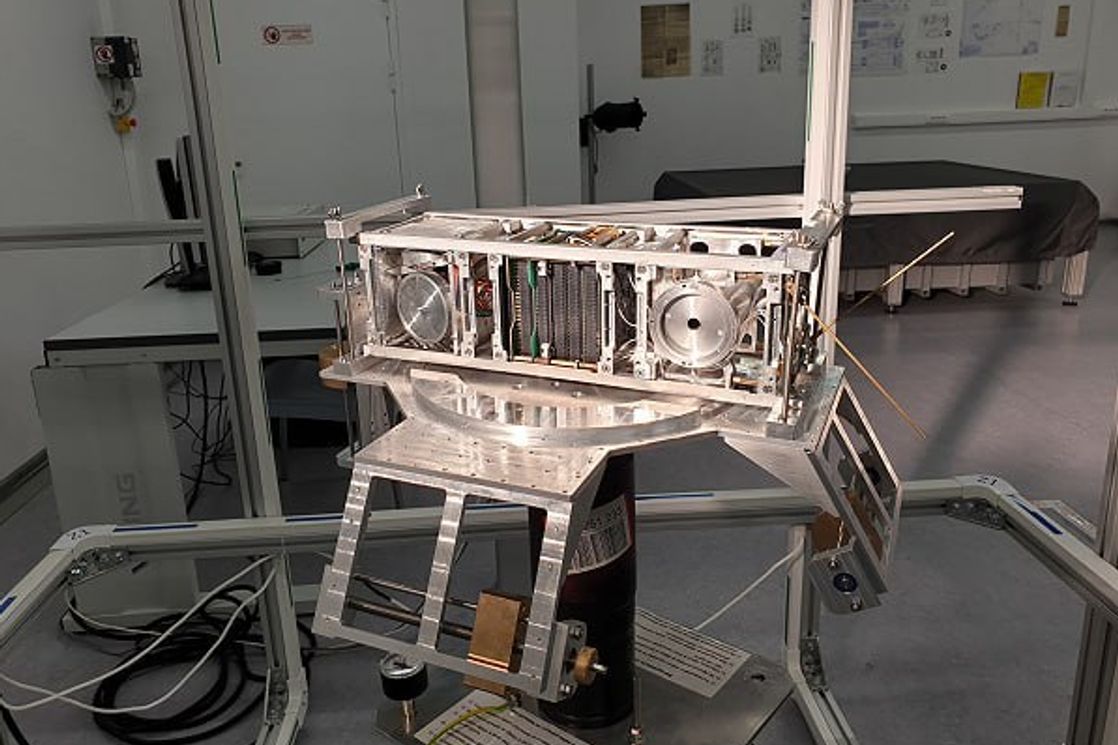
The reliability of the on-board electronics surpassed even optimistic forecasts: the total operating time of critical modules exceeded 35,000 hours without a single emergency restart. The chosen form of open channel, an AX.25 amateur radio format in the UHF range, played an important role. This meant that only the SatNOGS network of ground stations was able to receive and decrypt over 4,000 sessions (three leading observers monitored the broadcasts almost daily until the satellites’ orbits decayed), and each successfully decoded transmission appeared in real time in the open SatNOGS API.
The mission also served as a vibrant educational platform. Over the past four years, more than 15 students have taken part in the work of the MIEM Mission Control Centre, and Sirius students have had an opportunity to plan real orbital experiments for the first time, from drawing up daily transmission schedules to processing received telemetry. This experience gave rise to the idea of annual launches: in 2022 and 2023, CubeSX-HSE-2 and CubeSX-HSE-3 went into orbit with new payloads and improved modules.
The CubeSX-HSE and CubeSX-Sirius-HSE have achieved all their stated goals: demonstrating the performance of ultralight diffraction optics, collecting hundreds of valuable images, serving as an open data showcase for amateurs and professionals, and most importantly, training a new generation of small-spacecraft engineers. The CubeSats burned up at an altitude of about 80 km, but the code, data, and accumulated experience have already been passed on to the next participants of the Space-π programme. For them, the four-year record of the first university satellites is no longer an unattainable dream, but a new bar to pass.
Meanwhile, CubeSX-HSE-3, launched in June 2023, continues to operate in orbit. It transmits thousands of messages daily, and its telemetry confirms that the on-board electronics are operating normally and the solar panels are charging the batteries stably.
A new satellite will be sent into a Sun-synchronous orbit in the fourth quarter of 2025, while a sixth satellite focused on experiments with new materials is expected to be launched in 2026—thus tripling the amount of scientific data produced.

Dmitrii Abrameshin
Dmitrii Abrameshin, Head of the Mission Control Centre, Leading Engineer at the HSE Laboratory of Space Vehicles and Systems' Functional Safety, noted: ‘We demonstrated that HSE University can not only build a satellite, but also maintain its operation for a long time. CubeSX-HSE-3 has started providing fresh data for our archive, and the devices that we plan to launch in 2025 and 2026 will be capable of onboard data processing and prove that even a CubeSat can become a full-fledged orbital laboratory.’
See also:
New Method for Describing Graphene Simplifies Analysis of Nanomaterials
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has proposed a new mathematical method to analyse the structure of graphene. The scientists demonstrated that the characteristics of a graphene lattice can be represented using a three-step random walk model of a particle. This approach allows the lattice to be described more quickly and without cumbersome calculations. The study has been published in Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical.
Scientists Have Modelled Supercapacitor Operation at Molecular and Ionic Level
HSE scientists used supercomputer simulations to study the behaviour of ions and water molecules inside the nanopores of a supercapacitor. The results showed that even a very small amount of water alters the charge distribution inside the nanopores and influences the device’s energy storage capacity. This approach makes it possible to predict how supercapacitors behave under different electrolyte compositions and humidity conditions. The paper has been published in Electrochimica Acta. The study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
Designing an Accurate Reading Skills Test: Why Parallel Texts are Important in Dyslexia Diagnosis
Researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for accurately assessing reading skills in adults with reading impairments. It can be used, for instance, before and after sessions with a language therapist. The tool includes two texts that differ in content but are equal in complexity: participants were observed to read them at the same speed, make a similar number of errors, and understand the content to the same degree. Such parallel texts will enable more accurate diagnosis of dyslexia and better monitoring of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at addressing it. The paper has been published in Educational Studies.
HSE University Launches Development of Domestic 6G Communication Technologies Based on Sub-Terahertz Microelectronics
HSE University has launched a large-scale research and engineering initiative to develop domestic technologies for next-generation 6G communication systems. The project is being carried out by the team of the Strategic Technological Project 'Trusted 6G Communication Systems Technology Suite' implemented under the Priority 2030 programme.
Intellectual Capital in the Face of Shocks: Russia and Iran Explore Internationalisation
In today's issue of Schola, Mariya Molodchik, Senior Research Fellow at the International Laboratory of Intangible-Driven Economy and Professor at the School of Economics and Finance at HSE University’s Campus in Perm, discusses a joint project with Iran University of Science and Technology, titled 'Internationalization of Companies from Developing Countries: The Role of Intellectual Resources in Response to Exogenous Shocks.'
HSE Researchers Introduce Novel Symmetry-Aware Neural Network Architecture
Researchers at the HSE Laboratory for Geometric Algebra and Applications have developed a new neural network architecture that can accelerate and streamline data analysis in physics, biology, and engineering. The scientists presented their solution on July 16 in Vancouver at ICML 2025, one of the world's leading conferences on machine learning. Both the paper and the source code are publicly available.
Students from HSE and Other Universities Carry Out Research Expedition at New Chersonesos
As part of the Rediscovering Russia student expedition programme, HSE University organised a research trip under the framework of the School for Young Humanities Scholars to the New Chersonesos museum and church complex in Sevastopol. The results of this expedition will form the basis for proposals on educational projects aimed at shaping young people’s historical memory of the role of Chersonesos, Crimea, and the Byzantine legacy in the history of Russian culture and statehood.
HSE Researchers Determine Frequency of Genetic Mutations in People with Pulmonary Hypertension
For the first time in Russia, a team of scientists and clinicians has conducted a large-scale genetic study of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. The team, which included researchers from the International Laboratory of Bioinformatics at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science, analysed the genomes of over a hundred patients and found that approximately one in ten carried pathogenic mutations in the BMPR2 gene, which is responsible for vascular growth. Three of these mutations were described for the first time. The study has been published in Respiratory Research.
First Caucasus School on Experimental Research and Cognitive Sciences Takes Places in Adygea
On September 17–20, 2025, the First Caucasus School on Experimental Research and Cognitive Sciences took place at the Gornaya Legenda venue of Adyghe State University (ASU). The event was organised by the ASU Experimental Linguistics Laboratory, the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, and the HSE Centre for Sociocultural and Ethnolinguistic Studies. The school brought together over 50 participants—students, doctoral candidates, and early-career researchers from across Russia, along with lecturers and speakers from France, Serbia, China, Turkey, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan.
HSE Scientists Reveal How Disrupted Brain Connectivity Affects Cognitive and Social Behaviour in Children with Autism
An international team of scientists, including researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, has for the first time studied the connectivity between the brain's sensorimotor and cognitive control networks in children with autism. Using fMRI data, the researchers found that connections within the cognitive control network (responsible for attention and inhibitory control) are weakened, while connections between this network and the sensorimotor network (responsible for movement and sensory processing) are, by contrast, excessively strong. These features manifest as difficulties in social interaction and behavioural regulation in children. The study has been published in Brain Imaging and Behavior.


